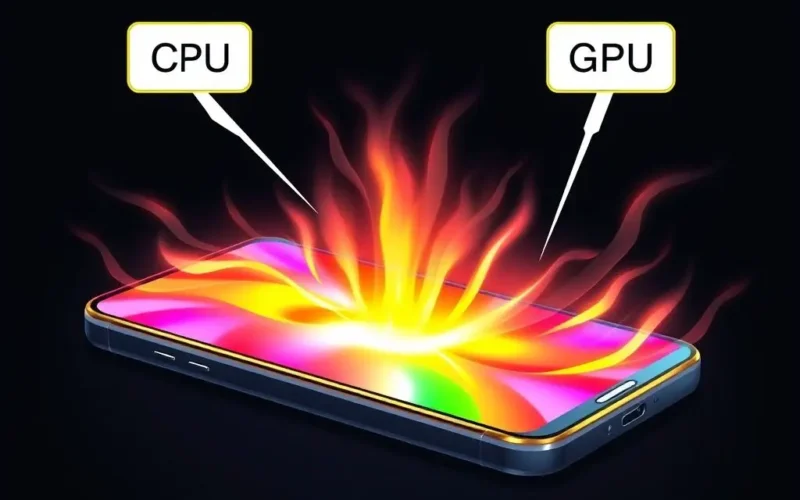
Ever gripped your phone mid-game and wondered if it was secretly moonlighting as a portable furnace? That scorching sensation is a universal experience for mobile gamers. While alarming, it’s usually your device telling you it’s working incredibly hard. The primary culprits behind this fiery feeling are your phone’s tiny powerhouses: the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
Think of your phone’s CPU as the brain, handling all the complex calculations, game logic, and general tasks. The GPU is the artist, specifically designed to render those stunning 3D environments, character models, effects, and textures you see on screen. When you fire up a graphically intense game, both the CPU and GPU are pushed to their absolute limits. They’re not just running; they’re sprinting a marathon at full speed, simultaneously processing millions of instructions and calculations every second.
This intense computational workout requires significant electrical energy. And whenever electrical energy flows through components, especially under heavy load, a byproduct is inevitably generated: heat. It’s a fundamental principle of physics – work generates energy, and some of that energy is released as heat due to electrical resistance within the circuits. The more demanding the task (like running the latest mobile game with high settings), the more power the CPU and GPU consume, and the more heat they produce.
Here’s a quick peek into why your phone turns into a heat sink:
Table of Contents
The Engine Room: CPU and GPU Under Load
Modern mobile games are incredibly sophisticated. They feature detailed graphics, complex physics engines, artificial intelligence (AI) for non-player characters, intricate animations, and large open worlds. Rendering just one frame of a 3D scene involves:
- CPU Tasks: Processing game logic, AI decisions, physics calculations (collisions, gravity), managing game state, handling user input, networking (for online games), and feeding instructions to the GPU.
- GPU Tasks: Taking the data from the CPU and rendering the visuals. This involves processing vertices (points in 3D space), texturing surfaces, applying shaders (for lighting, shadows, reflections), anti-aliasing (smoothing edges), and outputting the final image to the display.
Both components work in tandem, but graphics rendering is particularly taxing on the GPU. Higher resolutions, complex shaders, and more objects on screen mean the GPU has to perform vastly more calculations per second. The CPU is also busy, especially in games with lots of characters, complex simulations, or sophisticated AI.
This relentless cycle of processing and rendering, frame after frame, pushes these tiny silicon chips to their thermal limits. They are essentially operating like tiny supercomputers packed into a very confined space.
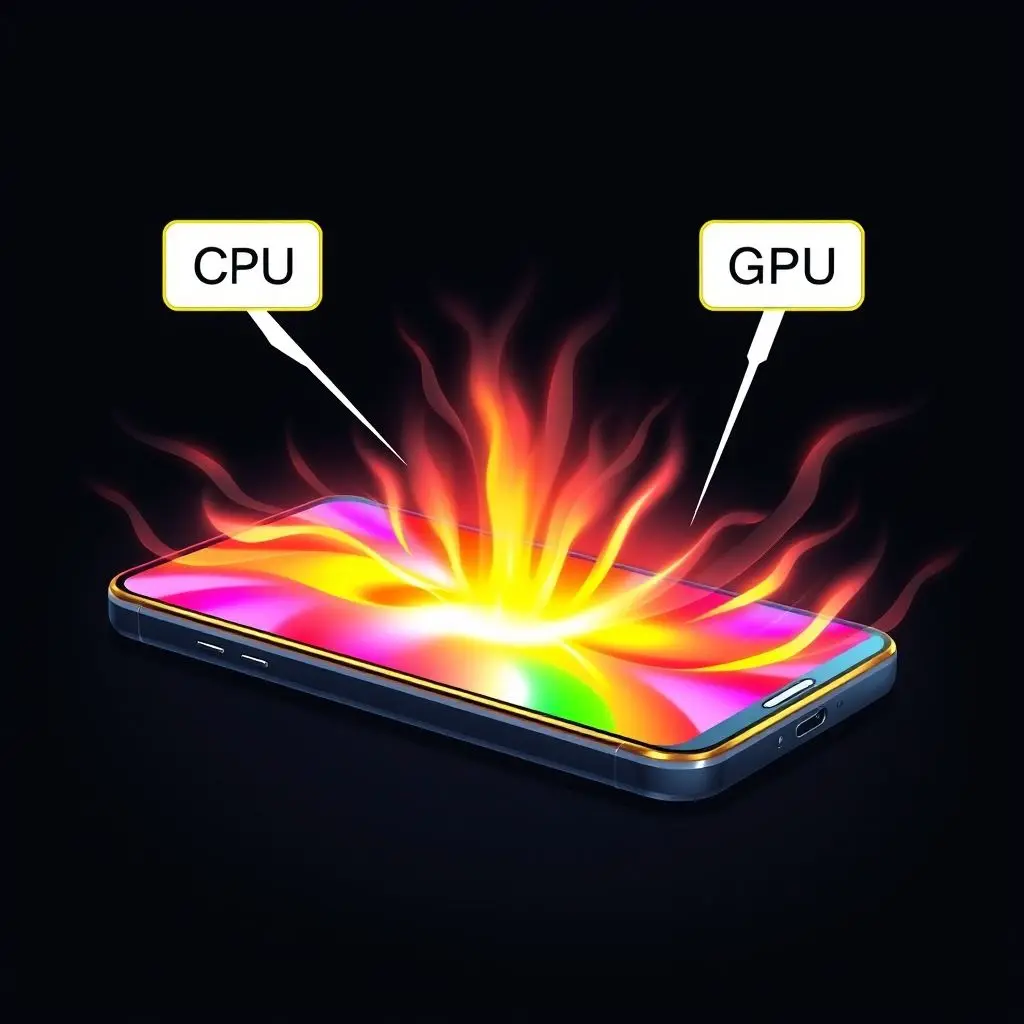

The Unavoidable Byproduct: Heat Generation
As mentioned, the conversion of electrical energy into computational work isn’t perfectly efficient. A significant portion is lost as heat. This heat is generated right at the source – within the transistors and pathways of the CPU and GPU chips themselves. While phones have basic thermal management systems (usually passive cooling using graphite sheets or vapor chambers in higher-end models), they are far less sophisticated than the active cooling systems (fans, large heatsinks) found in gaming PCs or consoles.
The heat then dissipates through the phone’s body. The metal frame and glass back often act as a large heatsink, which is why the phone feels hot to the touch – it’s effectively radiating the internal heat outwards.

The Phone’s Defense Mechanism: Thermal Throttling
Excessive heat is detrimental to electronic components. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can shorten their lifespan and even cause temporary instability or permanent damage. To protect itself, your phone’s operating system and hardware implement a safety feature called thermal throttling.
When sensors detect that critical components like the CPU and GPU are reaching a predefined temperature threshold, the system intentionally reduces their clock speeds (how many cycles they can perform per second). By slowing down, they consume less power and generate less heat. This brings the temperature back down to a safer level.
While essential for the phone’s health, throttling results in a noticeable drop in performance. Frame rates might decrease, graphics quality might be subtly reduced, and the overall gaming experience can become less smooth or responsive. That moment when your game suddenly feels sluggish after playing for a while? That’s likely thermal throttling kicking in.
Other Factors Contributing to Heat
While CPU and GPU load is the primary driver, other things can exacerbate the heat issue:
- Environment Temperature: Playing in a hot room or direct sunlight will make your phone heat up faster and reach throttling temperatures sooner.
- Charging While Gaming: Charging itself generates heat. Doing both simultaneously significantly increases the thermal load on the device.
- Protective Cases: Thick or poorly ventilated cases can trap heat, preventing it from dissipating efficiently through the phone’s body.
- Background Apps: Other apps running in the background, even if minimized, can consume resources and contribute to the overall workload and heat.
- Screen Brightness: A very bright screen consumes more power and generates a small amount of heat.
Sometimes, a visual explanation helps solidify the concept. Check out this short video that quickly illustrates the idea:
Is the Heat Damaging My Phone?
Generally, no. Your phone’s thermal management and throttling systems are designed to prevent damage. While prolonged exposure to *extreme* heat over months or years *can* theoretically impact battery health or component longevity, the occasional heating during intense gaming sessions followed by cooling down is usually within the device’s engineered tolerances. Think of it as occasionally redlining a car engine – it’s designed to handle bursts of high performance, but you wouldn’t want to do it constantly for hours on end.
If your phone feels *exceptionally* hot, gets stuck in a throttled state, or shows warning messages, it might be worth investigating further. But the typical warmth you feel during gaming is a normal operational characteristic.
Keeping Your Cool: Tips to Reduce Phone Heat While Gaming
While you can’t eliminate heat entirely during demanding games, you can mitigate it:
- Lower Graphics Settings: This is the most effective method. Reducing resolution, texture quality, effects, or disabling features like VSync significantly lowers the load on the GPU and CPU, directly reducing heat generation.
- Remove Your Case: If playing a long session, take off your phone case to allow for better heat dissipation.
- Close Background Apps: Ensure no unnecessary apps are running and consuming resources.
- Avoid Charging While Gaming: If possible, finish your gaming session before plugging in.
- Play in a Cooler Environment: Avoid direct sunlight and play in a room with air conditioning or good ventilation.
- Consider External Coolers: For serious mobile gamers, external phone coolers (often clip-on fans or Peltier effect coolers) can significantly help in dissipating heat and preventing throttling.

Frequently Asked Questions About Phone Heat and Gaming
Q: My phone gets hot even when not gaming. Why?
A: Other demanding tasks like video editing, streaming high-resolution video, using navigation apps for extended periods, or even background processes like app updates or malware scans can stress the CPU and GPU, leading to heat. A consistently hot phone even when idle could indicate a software issue or a hardware problem.
Q: Does restarting my phone help with heating?
A: Sometimes. Restarting can clear out rogue background processes or temporary software glitches that might be causing unnecessary load on the system, which in turn can reduce heat.
Q: Can phone games damage the battery by making it hot?
A: Batteries are sensitive to heat. While occasional heat from gaming is generally managed by the phone, consistently operating at high temperatures, especially combined with charging, can accelerate battery degradation over the long term, potentially reducing its overall capacity and lifespan.
Q: Why do some phones get hotter than others?
A: Different phones have different processors (some are more power-efficient), different internal designs (thermal dissipation varies), and different levels of performance they try to sustain before throttling. High-performance gaming phones usually have more advanced cooling systems but might also push components harder, leading to more noticeable heat.
Understanding Your Device’s Workout
The next time your phone feels like a hot potato during an intense gaming session, remember it’s not a fault; it’s a consequence of its powerful CPU and GPU working overtime to deliver that immersive experience. It’s your pocket-sized supercomputer putting in a serious shift. By understanding why it happens and taking a few simple steps, you can help your device manage the heat, ensuring smoother gameplay and potentially extending its overall health.





