Feeling a bit exposed online? Like your every click is out there on the wide-open digital highway? You’re not alone. We often hear terms like privacy, security, and encryption thrown around, and if you’ve ever wondered how to truly beef up your online defenses, you’ve likely stumbled upon the term ‘VPN’. So, what is a VPN, really? Imagine carving out your very own private, super-secure express lane right through the chaotic mess of the internet. Sounds intriguing, right? (It is!)
A VPN essentially scrambles your data, making it a jumbled mess to anyone trying to snoop – whether you’re on public Wi-Fi or just browsing from home. Think of it as an extra layer of privacy, a significant boost to your digital security, and sometimes, your golden ticket to accessing content that’s usually blocked in your region. It’s like a little bit of tech magic!
If you’re a visual learner or just fancy a super-quick rundown, we’ve actually boiled down the essence of VPNs into a nifty YouTube Short. It’s a bite-sized explainer that uses the ‘secure tunnel’ idea to make things crystal clear. Give it a whirl – it’s less than a minute but speaks volumes!
Pretty neat, huh? Now, let’s dive deeper and untangle exactly what a VPN is and how this ‘magic’ actually works.
Table of Contents
Decoding VPN: Virtual, Private, Network
So, VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. Let’s break that down, word by word, because each part is key to understanding its function:
- Virtual: This means the network isn’t made up of physical wires creating a direct connection between your computer and the server you’re trying to reach (like an old-school LAN cable). Instead, it creates a private connection over the existing public internet infrastructure. It’s a software-defined boundary, existing in code rather than copper.
- Private: This is the heart of it. Your activity within this ‘virtual’ network is kept private. How? Through sophisticated encryption methods that scramble your data. This means that even if someone (your Internet Service Provider, hackers on public Wi-Fi, or government agencies) intercepts your data, they won’t be able to understand it without the decryption key. It’s like sending a secret message in a code only you and your recipient know.
- Network: A VPN extends a private network across a public network. It allows your device to send and receive data as if it were directly connected to that private network, even though it’s physically somewhere else. This is crucial for accessing resources securely and appearing as if you’re browsing from a different location.
The Magic Tunnel: How a VPN Shields Your Data
The ‘secure tunnel’ analogy is a fantastic way to picture how a VPN operates. Imagine all the regular internet traffic whizzing by on a chaotic, multi-lane highway – exposed and visible. When you connect to a VPN, it’s like your data gets its own armored, private tunnel straight through this highway.
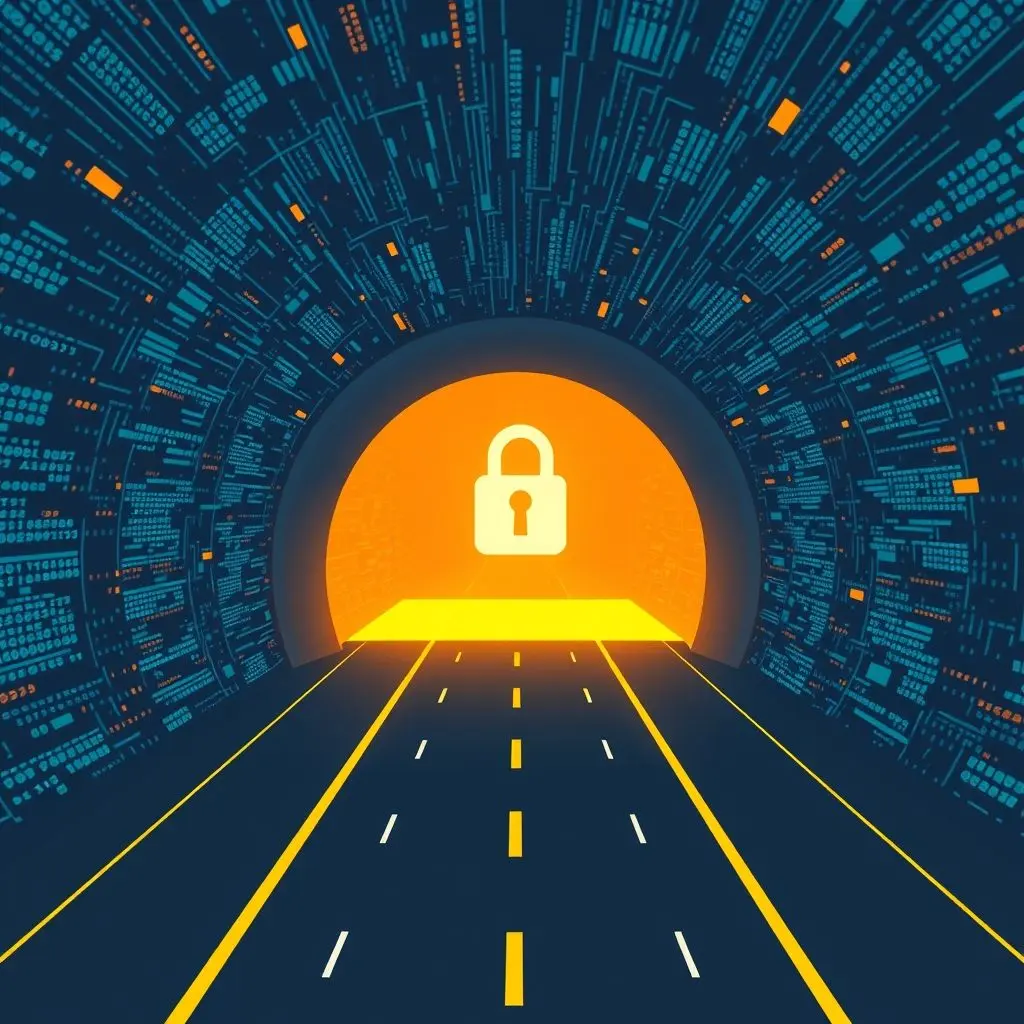

Here’s a step-by-step look at the journey your data takes:
- Initiation: You launch your VPN application (client) on your device (computer, smartphone, tablet).
- Connection: The VPN client establishes a secure, authenticated connection with a VPN server. This server could be located anywhere in the world, depending on your choice or the VPN provider’s setup.
- Encryption: Once the connection is live, all internet traffic from your device is routed through this VPN server. Before your data leaves your device, the VPN client encrypts it. Think of this as putting your data into an unbreakable digital safe. Common strong encryption protocols include OpenVPN and WireGuard®, often using AES-256 encryption, which is considered military-grade.
- Tunneling: Your encrypted data then travels through the internet to the VPN server. This journey is the ‘secure tunnel.’ Even if intercepted, the data is just gibberish to eavesdroppers.
- IP Masking: When your data reaches the VPN server, it’s decrypted. The VPN server then sends your request to the final destination website or online service. Critically, it does this using its own IP address, not yours. This masks your real IP address, making it appear as if your internet activity is originating from the VPN server’s location.
- The Return Trip: When the website or service responds, the data is sent back to the VPN server. The server encrypts it again and sends it back to your device through the secure tunnel. Your VPN client then decrypts the data for you to see.
This entire process happens in milliseconds, often with a negligible impact on your browsing speed, especially with premium VPN services.
Unlocking the Perks: Why You Might Need a VPN
Understanding how a VPN works is one thing, but why should you actually use one? The benefits are numerous and cater to a wide range of online activities.
1. Supercharged Online Privacy
In an age where data is the new gold, protecting your online privacy is paramount.
- Hide Your IP Address: Your IP address is like your home address online; it can reveal your general location and be used to track you. A VPN masks your real IP, replacing it with the IP of the VPN server, making it much harder to trace your activities back to you.
- Thwart ISP Tracking: Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can see every website you visit. While they might claim not to misuse this data, many log it and can be compelled to share it with authorities or even sell anonymized (and sometimes not-so-anonymized) versions to marketers. A VPN encrypts your traffic, so your ISP can see you’re connected to a VPN, but not what you’re doing online.
- Dodge Third-Party Snoops: Advertisers, social media platforms, and websites constantly try to track your browsing habits to build profiles for targeted ads or other purposes. A VPN makes this significantly more difficult.
2. Beefed-Up Digital Security
A VPN is a powerful ally in your cybersecurity arsenal.

- Safety on Public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi networks (in cafes, airports, hotels) are notoriously insecure. Hackers can easily set up fake hotspots or snoop on unencrypted connections to steal passwords, financial details, or other sensitive information. A VPN encrypts your connection, creating a secure bubble around your data, even on the sketchiest public networks.
- Protection from Certain Cyber Threats: While not a replacement for antivirus software, a VPN can protect you from some threats like Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks, where an attacker intercepts communication between two parties.
3. Access Without Borders: Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
Ever been frustrated by the “This content is not available in your region” message? A VPN can be your key.
- Unlock Streaming Libraries: Streaming services often have different content libraries for different countries due to licensing agreements. By connecting to a VPN server in another country, you can potentially access that country’s library. Disclaimer: Be sure to check the Terms of Service for any streaming platform, as using a VPN to bypass geo-restrictions might violate them.
- Overcome Censorship: In some countries, access to certain websites, social media platforms, or news outlets is restricted. A VPN can help bypass these censorship blocks by routing your traffic through a server in a country with fewer restrictions.
- Get Better Deals: Believe it or not, some online retailers, airlines, and booking sites show different prices based on your location (derived from your IP address). Experimenting with VPN servers in different locations might snag you a better deal.
4. Enhanced (But Not Absolute) Anonymity
While true, complete online anonymity is incredibly difficult to achieve, a VPN is a significant step in that direction.
- Masking Your Digital Footprint: By hiding your IP and encrypting your traffic, a VPN makes it harder for websites, advertisers, and snoopers to track your online movements and build a profile of you.
- The Importance of No-Logs Policies: For maximum privacy, choose a VPN provider with a strict, independently audited no-logs policy. This means they don’t keep records of your online activity, IP address, or connection timestamps. If they don’t log it, they can’t share it.
It’s crucial to understand that a VPN doesn’t make you invisible or invincible. If you log into an account (like Google or Facebook), that service still knows it’s you, regardless of your IP address. For activities requiring higher levels of anonymity, other tools like Tor Browser are often used in conjunction with, or instead of, a VPN.
VPNs in Action: Everyday Uses You Might Not Expect
VPNs aren’t just for tech wizards or digital privacy purists. They have practical applications for many everyday online tasks:
- Secure Remote Work: Many companies require employees to use a VPN to securely access the company’s internal network and sensitive data when working remotely. This creates a secure channel from the employee’s home to the office.
- Safe Online Banking and Shopping: When accessing your bank account or making online purchases, especially on unfamiliar networks, a VPN adds an extra layer of security, encrypting your financial details and login credentials.
- Protecting Sensitive Research: Journalists, activists, and researchers often use VPNs to protect their communications, research activities, and sources, especially when dealing with sensitive or controversial topics.
- Better Gaming Experience: Gamers can use VPNs to potentially reduce ping and lag by connecting to a server closer to the game server. They can also access games or game servers that are region-locked or released earlier in other countries. Some VPNs also offer protection against DDoS attacks.
- Avoiding Bandwidth Throttling: Some ISPs may slow down (throttle) your internet speed for certain types of traffic, like streaming or torrenting. A VPN can sometimes help bypass this by encrypting your traffic, making it harder for your ISP to identify and throttle specific activities.
The Flip Side: Potential VPN Drawbacks and Considerations
While VPNs offer significant advantages, there are a few potential downsides and important factors to keep in mind:
- Potential Speed Reduction: Encrypting and routing your traffic through an extra server can sometimes slow down your internet connection. However, premium VPNs with optimized servers often have a minimal impact, and sometimes, if your ISP is throttling you, a VPN might even improve speeds for certain activities.
- Cost: Free vs. Paid VPNs:
- Paid VPNs: Reputable paid VPNs generally offer better security, faster speeds, more server locations, and crucial features like no-logs policies and kill switches (which cut your internet if the VPN connection drops). They invest in their infrastructure and privacy practices.
- Free VPNs: Be very cautious with free VPNs. Running a VPN service costs money. If you’re not paying with cash, you might be paying with your data. Some free VPNs log user activity, sell data to third parties, bombard you with ads, have limited bandwidth/speed, or even contain malware. There are a few trustworthy freemium models from reputable providers, but thorough research is essential.
- Legality: Using a VPN is legal in most countries. However, any illegal activity conducted online remains illegal, whether you’re using a VPN or not. Some countries with strict internet censorship (e.g., China, Russia, Iran) heavily regulate or ban VPN use, so it’s important to be aware of local laws if you’re in such a region. Disclaimer: This information is for general guidance only and not legal advice. Always check the specific laws of your country.
- Choosing a Reputable Provider: Not all VPNs are created equal. It’s vital to choose a trustworthy provider with a proven track record, a clear privacy policy (preferably no-logs and independently audited), strong encryption, a wide range of server locations, and good customer support. Do your research!
- VPN Blocking: Some websites and services actively try to block VPN connections. This is common with some streaming platforms that are strict about geo-restrictions. While good VPNs are adept at overcoming these blocks, it can sometimes be a cat-and-mouse game.
The VPN Spell Book: Key Takeaways
So, to quickly recap the ‘VPN magic’ we’ve discussed:
- A VPN creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for your internet traffic.
- It enhances your online privacy by masking your IP address and preventing ISP/third-party tracking.
- It boosts your digital security, especially on public Wi-Fi.
- It can help you bypass geo-restrictions and access a wider range of online content.
- It routes your traffic through a remote server, making it appear as if you’re browsing from that server’s location.
Essentially, a VPN puts you more in control of your digital life by adding crucial layers of privacy and security.
Your VPN Questions Answered: FAQ
Is using a VPN legal?
In most countries, yes, using a VPN is perfectly legal. However, using a VPN to conduct illegal activities is still illegal. A few countries have restrictions or bans on VPNs, so it’s wise to be aware of the laws in your specific location or any country you plan to visit.
Can a VPN make me completely anonymous?
No, a VPN significantly enhances your privacy but doesn’t make you 100% anonymous. Your browsing can still be linked to you if you log into personal accounts or through other tracking methods like browser fingerprinting. For higher levels of anonymity, tools like Tor are often used, sometimes in conjunction with a VPN (though this is an advanced setup).
Will a VPN slow down my internet?
It can, as your data takes a slightly longer route and undergoes encryption/decryption. However, with top-tier VPN services, the speed reduction is often minimal and barely noticeable for most activities. In some cases, if your ISP is throttling certain types of traffic, a VPN might even improve your speed for those activities.
Are free VPNs safe to use?
Generally, it’s best to be very cautious with free VPNs. Running a VPN service is expensive, so free providers often monetize through other means, such as selling your data, showing intrusive ads, or even bundling malware. While a few reputable ‘freemium’ VPNs exist (offering a limited free version of their paid service), always do thorough research before trusting a free VPN with your data.
How do I choose a good VPN?
Look for a VPN provider with:
- A strict, independently audited no-logs policy.
- Strong encryption protocols (e.g., OpenVPN, WireGuard® with AES-256).
- A wide network of fast servers in diverse locations.
- A kill switch feature.
- User-friendly apps for your devices.
- Good customer support.
- Positive reviews from reputable tech sources and users.
Is a VPN Right for You? Taking Control of Your Digital Journey
In today’s digitally interconnected world, understanding tools like VPNs is more important than ever. Whether you’re looking to safeguard your privacy on public Wi-Fi, secure your sensitive data, or simply explore a more open internet, a Virtual Private Network offers a powerful solution. It’s about reclaiming a bit of control over your online experience, wrapping your digital self in a cloak of security and privacy.
While not a silver bullet for all online threats, a VPN is a fundamental tool for anyone serious about their digital well-being. Hopefully, this guide has demystified the ‘what,’ ‘why,’ and ‘how’ of VPNs, and you now feel more equipped to decide if one is right for you.
Have you used a VPN? What are your favorite benefits or tips? Share your thoughts in the comments below – let’s keep untangling the tech world together!