Ever found yourself absolutely mesmerized by an image that seemingly popped into existence from a simple line of text? You type “a cat riding a unicorn on the moon,” and poof! There it is. It feels like magic, right? As if the AI just peered into your wildest daydreams and plucked out a visual. The truth is, it’s less about sorcery and more like an incredibly sophisticated form of digital sculpting, where your words guide the artist’s hand.
Think of it like this: the AI starts with a completely blank canvas, or rather, a canvas filled with what looks like old-school TV static – pure digital noise. Your text prompt, say something wonderfully whimsical like ‘a synthwave Corgi DJ,’ acts as the detailed instruction manual. The AI, having “studied” an astronomical number of images from the internet, starts to recognize the concepts – ‘Corgi,’ ‘DJ,’ ‘synthwave.’ It then meticulously begins to remove the noise, bit by bit, refining the chaos until only your Corgi DJ masterpiece emerges. It’s a fascinating dance of turning utter randomness into something remarkably cool, all based on your creative direction.
Mind already a little boggled? If you’re a visual learner or just fancy a super-swift summary, we’ve got a YouTube Short that boils this down in under 60 seconds. Give it a watch before we delve deeper into the digital wizardry!
Table of Contents
The Starting Point: A Canvas of Chaos
It might sound counterintuitive, but many of the most advanced AI image generators begin their creative process not with a blank slate, but with a screen full of random pixels – pure, unadulterated digital noise. Imagine that static snow you used to see on an untuned TV channel. That’s the primordial soup from which your vibrant image will eventually emerge.

Why start with chaos? This approach, central to a popular technique called Diffusion Models, is about refinement. It’s easier for the AI to learn how to remove noise to arrive at a coherent image that matches your text prompt than to build an image from absolute nothingness in one go.
Your Words are the AI’s Chisel: The Role of Text Prompts
So, you have this field of noise. Now what? This is where your creativity comes in! The text prompt you provide is the single most crucial piece of guidance for the AI. Phrases like “a majestic lion wearing a crown, photorealistic” or “a cyberpunk cityscape at dusk, neon lights reflecting on wet streets, anime style” are the blueprints the AI uses.
The AI, through its extensive training, has learned to associate words and phrases with visual elements, styles, and compositions. When you give it a prompt, it essentially translates those words into a target “look” and then begins the process of shaping the noise towards that target.
The Denoising Dance: How Diffusion Models Work Their Magic
This is where the “sculpting” truly happens. Diffusion Models work by progressively removing the noise from the initial static-filled image in a series of steps. Think of it like an archaeologist carefully brushing away dirt to reveal a hidden artifact.
- Noise Overload: The process actually starts by taking real images during its training phase and deliberately adding noise to them, step-by-step, until they become pure static. This teaches the AI what noise looks like and how it obscures an image.
- Learning to Reverse: The AI is then trained to reverse this process. It learns to predict and remove the noise it just saw being added, gradually recovering the original image.
- Guided by Your Prompt: When you give it a text prompt for a new image, the AI starts with a fresh patch of random noise. Then, using what it learned about denoising and its understanding of your text prompt, it meticulously subtracts noise in a way that steers the emerging image towards your description.
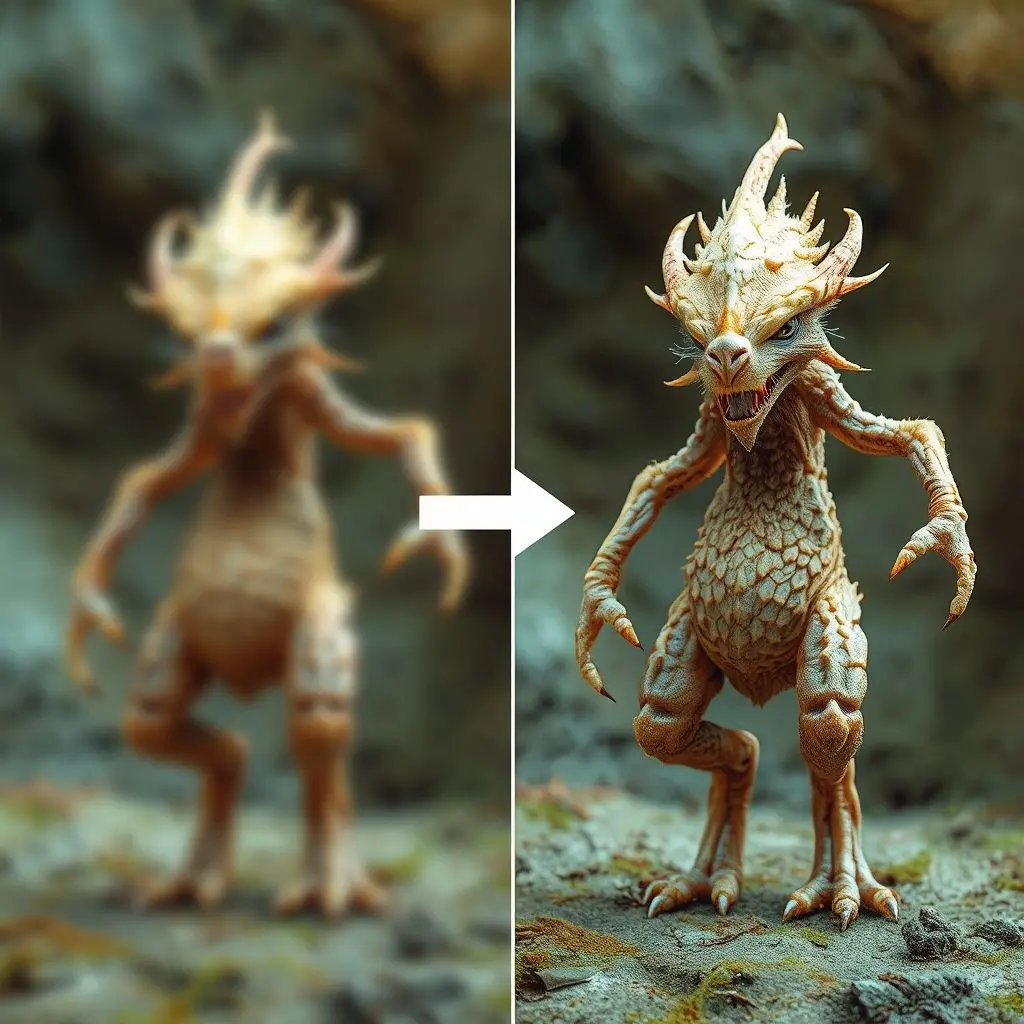

Each step refines the image a little more, bringing details into focus, correcting colors, and shaping forms, until the initial chaos transforms into the ‘synthwave Corgi DJ’ or whatever masterpiece you envisioned.

What About Other AI Image Models? A Quick Peek at GANs
While Diffusion Models are currently very popular and effective, they aren’t the only game in town. You might have also heard of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). These were a dominant force in AI image generation for a while and work on a fascinating “cat and mouse” principle:
- The Generator: This part of the AI tries to create realistic images. Think of it as an art forger trying to create a convincing fake.
- The Discriminator: This part of the AI acts as an art critic. Its job is to look at images (both real ones from the training data and fakes from the Generator) and decide if they are real or AI-generated.
The Generator and Discriminator are trained together. The Generator constantly tries to fool the Discriminator, and the Discriminator gets better at spotting fakes. This competitive process pushes the Generator to produce increasingly realistic and high-quality images. While incredibly clever, GANs can sometimes be trickier to train and control compared to the latest Diffusion Models for certain types of image generation tasks.
The Secret Sauce: The Immense Power of Training Data
None of this would be possible without the AI’s “education.” When we say the AI has “studied millions of images,” we’re talking about massive datasets. These datasets can contain billions of image-text pairs (like a picture of a cat with the caption “a photo of a cat”).
By processing this colossal amount of visual and textual information, the AI learns intricate patterns, associations, and relationships:
- It learns what a “Corgi” looks like from countless Corgi pictures.
- It learns the aesthetic of “synthwave” by analyzing images tagged with that style.
- It figures out how to combine these concepts – a Corgi, in a synthwave style, acting as a DJ.
The quality and diversity of this training data are paramount. The more comprehensive and well-described the data, the better the AI becomes at understanding nuanced prompts and generating accurate, creative results.
Disclaimer: The specifics of datasets used by commercial AI models are often proprietary. The general principle, however, relies on vast quantities of publicly available or licensed image-text data.
So, Is It Actually “Thinking” or Creating Art?
While it’s tempting to anthropomorphize these AI models and say they “understand” or “create” in the human sense, it’s more accurate to say they are incredibly sophisticated pattern-matching and transformation engines. They don’t have consciousness, intent, or genuine understanding like humans do.
They are, however, powerful tools that can augment human creativity in astounding ways. The “art” comes from the collaboration: your imaginative prompt and the AI’s ability to translate that into a visual representation based on its training. Sometimes, they can even surprise us with interpretations we didn’t expect, leading to new creative avenues!
Limitations do exist. AI image generators can struggle with complex concepts like rendering anatomically correct hands, generating legible text within images, or perfectly understanding highly abstract or nonsensical prompts. But the field is evolving at a breakneck pace!
From Chaos to Cool: The Future is Visual
And there you have it – a simplified peek behind the digital curtain of AI image generation! It’s a journey from a jumble of random noise to a coherent, often stunning, visual piece, all guided by the power of your words and the “learned experience” of the AI. It’s not quite magic, but the results can certainly feel magical.
The ability to conjure images from thought is transforming creative industries, art, design, and even just everyday fun. So next time you prompt an AI to create something wild, remember the intricate dance of data, algorithms, and a little bit of structured chaos that makes it all happen. Pretty mind-bending, isn’t it?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q1: How does AI know what a ‘cat’ or ‘synthwave’ looks like?
- A: AI models are trained on vast datasets containing millions or even billions of images, many of which are labeled with descriptions. By analyzing these, the AI learns to associate words like ‘cat’ with the visual features of cats, and stylistic terms like ‘synthwave’ with the colors, shapes, and moods common to that aesthetic.
- Q2: What are Diffusion Models in AI image generation?
- A: Diffusion Models start with an image of random noise and gradually refine it by removing the noise step-by-step. Each step is guided by the text prompt, steering the image towards the desired output. It’s like sculpting by removing material rather than adding it.
- Q3: Are AI image generators easy to use?
- A: Many modern AI image generation tools are designed with user-friendly interfaces. You typically just need to type a text prompt. However, mastering “prompt engineering” – crafting effective prompts to get the exact results you want – can take some practice and experimentation.
- Q4: Can AI create any image I can imagine?
- A: While AI image generators are incredibly powerful, they do have limitations. They might struggle with highly complex or abstract concepts, specific details like the number of fingers on a hand, or generating coherent text within an image. However, their capabilities are constantly improving.
- Q5: What’s the difference between Diffusion Models and GANs?
- A: Both are methods for AI image generation. GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) use two competing neural networks (a generator and a discriminator) to create images. Diffusion Models, on the other hand, work by starting with noise and systematically removing it based on a text prompt to form an image. Diffusion models have recently become very popular due to their ability to generate high-quality and diverse images.