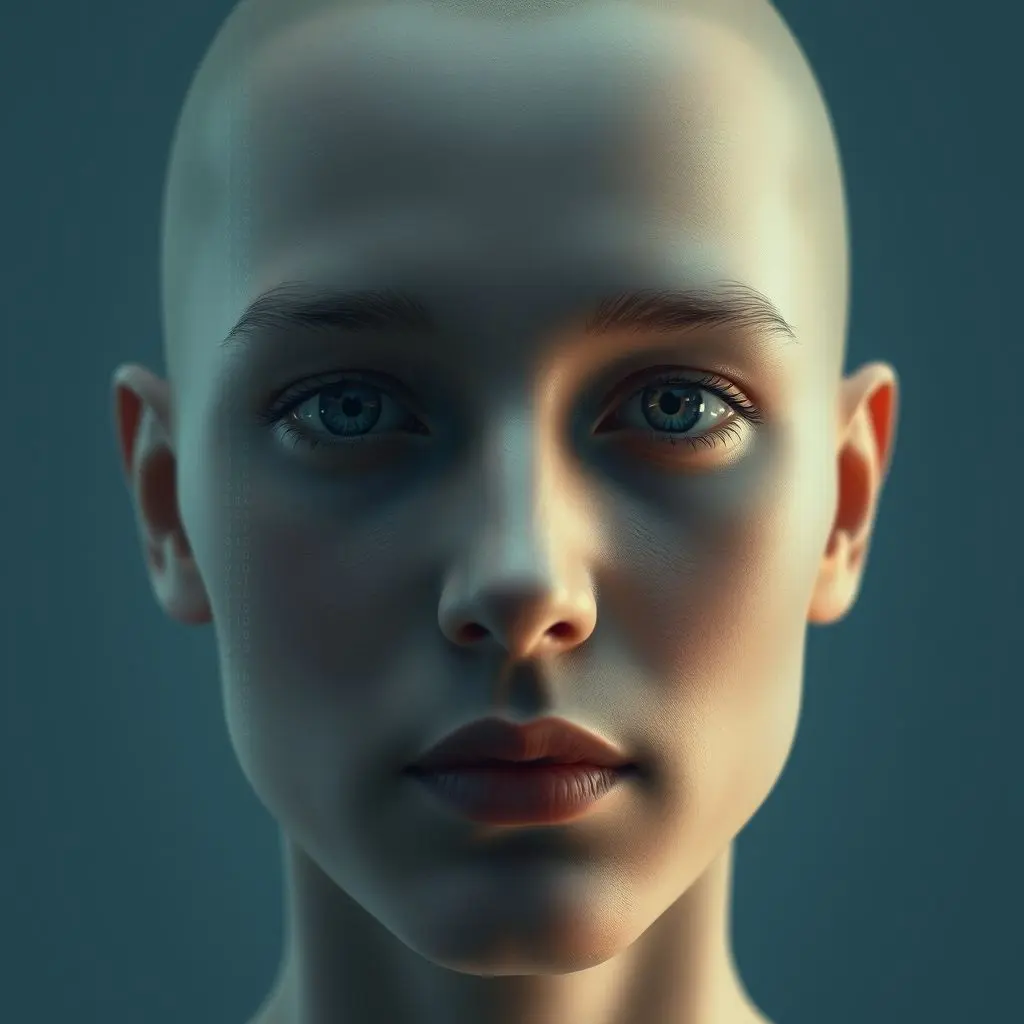
Forget those blocky figures and cartoonish profiles you’ve been stuck with online. What if your digital presence wasn’t just an avatar, but a hyper-realistic version of you? Imagine a digital twin that mirrors your expressions, your style, perhaps even your gait. The age of simple digital representations is rapidly evolving, propelled by incredible advancements in Artificial Intelligence.
AI isn’t just mastering board games or writing text anymore; it’s becoming a pixel-perfect sculptor. We’re moving beyond cute filters and stepping into a world where algorithms can construct incredibly lifelike human avatars from seemingly thin air, or perhaps just a few source images.
Want a sneak peek at just how eerily real these creations are starting to look? Check out this quick visual:
That glimpse hints at the potential. These aren’t just static images; the goal is dynamic, breathing digital identities. This isn’t confined to the realm of futuristic sci-fi anymore; it’s happening now, opening up possibilities across various fields you might not have even considered.
Table of Contents
How AI Breathes Life into Pixels: The Tech Behind the Avatar
Creating a truly realistic human avatar is a monumental task. It’s not just about getting the features right; it’s about capturing the subtle nuances that make us human – the tiny crinkles around the eyes when we smile, the way light plays on skin, the natural flow of hair, the unique expressions that convey emotion.
Several cutting-edge AI technologies are converging to make this possible:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): These have been instrumental in generating realistic images. A GAN involves two neural networks, a ‘generator’ that creates the image and a ‘discriminator’ that tries to detect if the image is fake. They train each other, with the generator constantly improving until it can fool the discriminator, resulting in incredibly convincing synthetic images.
- Diffusion Models: More recently, diffusion models have pushed the boundaries of image generation quality and diversity. They work by starting with random noise and iteratively ‘denoising’ it based on a prompt or condition (like generating a specific face) until a clear, coherent image emerges. Think of it like slowly revealing a photo from static.
- Neural Rendering: This technique focuses on synthesizing new views or complex scenes from limited input. Applied to avatars, it helps create consistent, realistic appearance from different angles and under varying lighting conditions, crucial for interactive 3D environments.
- NeRF (Neural Radiance Fields): A specific type of neural rendering that can reconstruct 3D scenes from 2D images, allowing for photorealistic rendering from any viewpoint. While computationally intensive, it’s being adapted for dynamic scenes and characters.
These models are trained on vast datasets of human faces, bodies, and expressions. The sheer scale and complexity of this data, combined with ever-increasing computational power, allow the AI to learn the intricate patterns and structures that define human appearance down to the pore level.
![]()
The Uncanny Valley and Beyond: Challenges in Crafting Digital Doubles
While the results are impressive, achieving true, indistinguishable realism is incredibly challenging. AI-generated faces can easily fall into the ‘uncanny valley’ – that unsettling feeling we get when something looks *almost* human but is just slightly off, making it appear strange or even creepy.
Overcoming the uncanny valley requires mastering subtleties:
- Micro-expressions: The fleeting, involuntary facial movements that reveal true emotion are notoriously difficult to replicate authentically.
- Hair and Clothing: Simulating the physics of hair strands and fabric wrinkles, and how they interact with light and movement, remains complex.
- Realistic Lighting and Shadows: Integrating avatars seamlessly into different lighting environments requires sophisticated rendering that few models have perfected.
- Consistency: Ensuring the avatar looks consistent from every angle and maintains its likeness during movement and speech is vital for applications like video calls or virtual interactions.
- Authentic Likeness vs. Generic Faces: Generating a *new* realistic face is one thing; accurately replicating the unique likeness of a specific individual is another, often requiring detailed scans or multiple reference images and still posing challenges for perfect fidelity.
AI models are constantly improving, learning from errors and leveraging more sophisticated architectures to tackle these hurdles, inching closer to creations that are truly convincing.
More Than Just a Profile Picture: Unlocking New Realities
So, what exactly can we *do* with these incredibly realistic digital humans? The possibilities stretch far beyond just having a cool online avatar. Think about:
- Next-Level Communication: Imagine video calls where your avatar perfectly mirrors your expressions and body language, creating a much more engaging and personal virtual interaction, especially in VR or AR environments.
- Personalized Virtual Assistants: Instead of a disembodied voice, interact with a digital assistant that has a realistic, approachable human face, potentially enhancing user experience and trust.
- Education and Entertainment: Bringing historical figures to life in documentaries or virtual reality experiences, allowing people to seemingly interact with individuals from the past. Creating unique, compelling characters for video games, films, or interactive stories that have a level of realism previously requiring extensive motion capture and 3D modeling.
- Creative Storytelling: Empowering content creators, from indie game developers to filmmakers, to populate their virtual worlds and narratives with diverse, realistic characters without the prohibitive costs of traditional methods.
- Virtual Try-Ons and E-commerce: Seeing how clothes, makeup, or accessories look on a digital double of yourself could revolutionize online shopping.
- Training Simulations: Creating realistic human characters for complex training scenarios in fields like healthcare or customer service.
![]()
These avatars can act as digital proxies, allowing us to interact in virtual spaces or with digital content in ways that feel more natural and intuitive.
The Ethical Maze: Navigating the Implications of Realistic AI Avatars
With great power comes significant responsibility. The ability to create hyper-realistic digital humans raises serious ethical questions that need careful consideration.
Deepfakes and Misinformation: The most immediate concern is the potential for misuse. Realistic AI avatars can be used to create convincing ‘deepfakes’ – synthetic media where a person’s likeness is digitally manipulated to say or do things they never did. This poses a significant threat for spreading misinformation, defamation, and non-consensual intimate imagery.

- Privacy and Consent: Training these models often requires vast amounts of data. Ensuring this data is sourced ethically and used with proper consent is paramount. Creating a digital twin of someone requires explicit permission.
- Identity Theft and Fraud: Realistic digital doubles could potentially be used for malicious purposes like bypassing biometric security or impersonating individuals online.
- Bias: If the training data is biased (e.g., lacks diversity), the resulting avatars may perpetuate those biases, leading to underrepresentation or misrepresentation of certain groups.
- Ownership and Rights: Who owns a digital avatar created by AI? What rights do individuals have over their digital likeness if used to train or generate avatars? These are new legal and ethical frontiers.
Developing robust detection methods for AI-generated content, establishing clear legal frameworks, and promoting ethical guidelines for AI development and use are crucial steps in mitigating these risks.
Creating Your Own Digital Persona (Or Imagining One)
While creating a movie-quality, perfectly lifelike avatar of *yourself* still often requires specialized scanning technology and significant processing, AI is making the process more accessible for generating *new* realistic faces and characters.
Emerging tools and platforms are beginning to offer capabilities for generating realistic digital humans, sometimes from simple text descriptions or reference images. As the technology improves and becomes more democratized, the ability to craft your own detailed digital identity or create characters for your projects will become increasingly commonplace.
Where Do We Go From Here?
The journey towards truly indistinguishable AI-generated human avatars is ongoing. The technology is advancing at a breathtaking pace, continuously refining its ability to capture and recreate the essence of human appearance and behavior.
This capability will undoubtedly reshape how we interact with technology, with each other in digital spaces, and even how we perceive identity online. It opens up fascinating new avenues for creativity, communication, and exploration, while simultaneously demanding careful consideration of the ethical landscape we are stepping into. The future of digital identity isn’t static; it’s a dynamic, evolving canvas painted by algorithms, and seeing what emerges next is truly captivating.
FAQs About Realistic AI Avatars
Q: How realistic can AI avatars get?
A: Very realistic, sometimes indistinguishable from photos of real people in still images. Dynamic realism (movement, speech, expressions in real-time) is still improving but making significant strides.
Q: Is it possible to create a realistic avatar of myself using AI?
A: Yes, with the right technology. Some professional services use scanning combined with AI refinement. Consumer-level tools are emerging but creating a perfect likeness from just a few photos is still challenging for true realism compared to professional methods.
Q: What are the main risks associated with this technology?
A: The primary risks include the creation of malicious deepfakes for misinformation or harassment, privacy violations through misuse of data, and potential for identity theft or fraud.
Q: How is this different from avatars in video games?
A: While game avatars are becoming more detailed, AI-generated realistic avatars often aim for photorealism and biological accuracy down to skin texture and subtle movements, surpassing the typical stylized or less detailed rendering of many game characters, especially those customizable by users.
Q: Can AI avatars show real emotions?
A: AI avatars can be animated to *display* expressions that look like emotions, sometimes driven by a human operator’s movements (motion capture) or by algorithms attempting to interpret and replicate emotional cues from text or voice. Whether they *feel* emotions is a philosophical question well beyond current AI capabilities; they simulate, not feel.
Q: What industries will be most impacted by realistic AI avatars?
A: Gaming, entertainment (film/TV), virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), e-commerce, digital marketing, remote work/communication, and education are among the key sectors poised for transformation.