You walk over them every day, often without a second thought. Those ubiquitous, heavy, circular plates embedded in our streets and sidewalks — manhole covers. But have you ever paused to wonder why they’re almost always round? Is it a mere aesthetic choice, a legacy design, or something far more profound? The truth, as you’re about to discover, lies in a brilliant fusion of geometry, physics, and a deep understanding of urban engineering. It’s a perfect example of design where form unequivocally follows function, making them a testament to ingenious, life-saving design.
This seemingly simple circle is, in fact, a marvel of engineering. If you prefer a quick visual summary of this fascinating topic, we’ve got a YouTube Short that perfectly encapsulates the brilliance. Take a moment to watch it here:
Now, let’s dive deeper into why this circular shape isn’t just a design preference, but a critical safety feature.
Table of Contents
Safety First: The Inherent Geometry of Trust
The primary, undisputed reason for the roundness of manhole covers is simple geometry, directly translating to paramount safety. A round manhole cover, regardless of how it’s oriented, can never fall through its own circular opening. This is because the diameter of the cover is equal to the diameter of the opening, and a circle has a constant width across its entire form.
Imagine trying to drop a square cover into a square opening. If you turn it diagonally, the diagonal length of the square is greater than its side length. This means a square cover could potentially fall through a square opening of the same side length if it’s tilted into the diagonal position. The same principle applies to triangles or any other polygon with varying widths.
This isn’t a trivial detail. Manholes provide access to crucial underground utilities: sewers, telecommunication lines, electrical conduits, and more. Workers regularly enter these subterranean spaces. An unsecured or improperly seated cover that falls in could lead to catastrophic accidents, injuring workers below or creating dangerous open hazards for pedestrians and vehicles above. The round design eliminates this risk entirely, acting as a foolproof safety mechanism.

Beyond Safety: A Multitude of Engineering Advantages
While safety is paramount, the genius of the round manhole cover extends far beyond preventing falls. Several other engineering and logistical advantages cement its status as the "perfect tech design."
Effortless Movement and Transportation
Think about the sheer weight of these covers, often made of cast iron or reinforced concrete. A round cover can be easily rolled by a single worker. Try rolling a square or triangular slab of equivalent weight — it’s cumbersome, requires lifting, and often needs multiple people or specialized equipment. The ability to simply roll a cover saves time, reduces worker strain, and minimizes the risk of injury during maintenance or installation.
This is a subtle but significant ergonomic benefit often overlooked in complex engineering discussions.
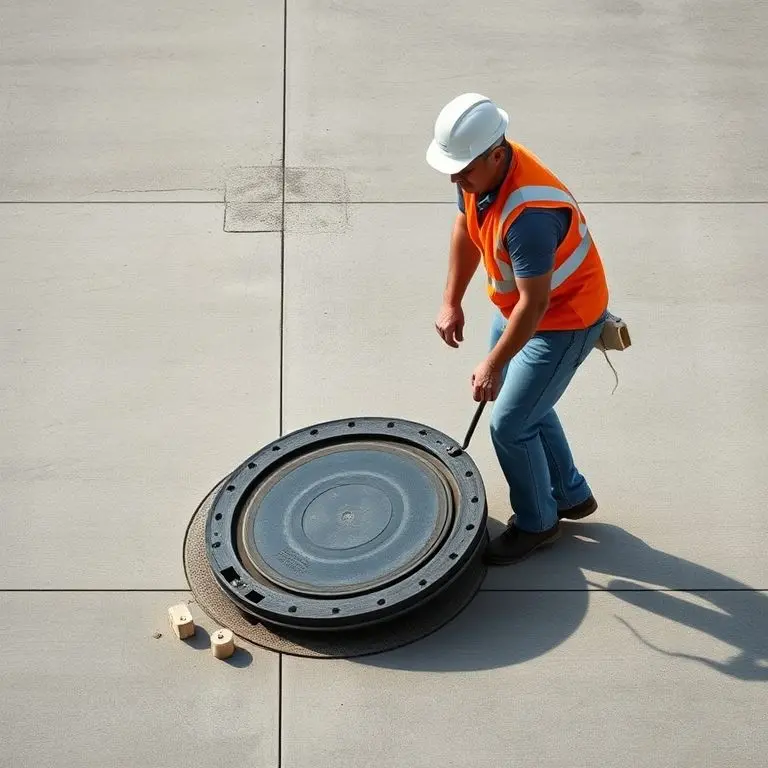

Superior Structural Integrity and Pressure Distribution
A circle is inherently one of the strongest geometric shapes. When pressure is applied evenly to its surface — say, from heavy vehicles driving over it — the forces are distributed uniformly along the entire circumference. This even distribution of stress minimizes localized weak points, making round covers incredibly resistant to deformation, cracking, and fatigue over time.
In contrast, square or rectangular covers have corners, which are natural stress concentration points. Under repeated heavy loads, these corners are far more susceptible to cracking and failure, compromising the cover’s lifespan and safety. This principle is vital for elements subjected to dynamic loads, like those in urban traffic.
Simplified Manufacturing and Cost-Effectiveness
Casting round objects is generally simpler and more efficient than casting complex polygonal shapes. The molds are easier to create, maintain, and the casting process often results in fewer defects due to the absence of sharp internal angles where stress can build during cooling.
Machining a circular edge to create a tight fit with its frame is also straightforward with modern lathes and CNC machines. This efficiency in manufacturing translates directly into lower production costs, making round covers a more economical choice for widespread urban deployment.
Optimal Sealing Against the Elements
Maintaining a tight seal around an opening is crucial to prevent ingress of debris, rainwater, and unwanted gases from below (like methane in sewer systems). A circular mating surface allows for a consistent, continuous seal that is easier to achieve and maintain than one with multiple corners.
Gaskets and sealing compounds adhere more effectively to a smooth, uninterrupted curve, providing superior protection against contaminants and odor leakage. This enhances the sanitation and longevity of the underground infrastructure.
Weight Distribution and Handling
While we talked about rolling, consider the weight itself. The circular shape inherently allows for better material distribution for a given opening size, often making it lighter for the same strength compared to an angular cover that might need extra reinforcement at corners. When a cover must be lifted, the even weight distribution makes it less awkward to handle, even if still heavy.
Are All Manhole Covers Round? The Exceptions
While the vast majority of manhole covers you encounter are round, it’s worth noting that not every access cover is. You might occasionally see square or rectangular covers, particularly for utility boxes that house electrical junction points, telecommunication cables, or water meters.
The reason these exceptions exist is usually because the equipment inside is rectangular and a square opening allows for easier access or removal of the internal components. However, these are often designed differently, sometimes hinged, bolted down, or are located in areas with less traffic and therefore less risk of dynamic load stress or falling through. Critically, these covers are generally not for accessing deep shafts where a worker might be present below the opening, mitigating the primary safety concern.

The Testament to Thoughtful Engineering
The humble manhole cover is a brilliant yet often unappreciated piece of engineering. Its circular form isn’t a coincidence or an aesthetic whim; it’s a meticulously chosen design born from practical necessities, rigorous safety standards, and fundamental principles of physics and geometry. It’s a prime example of how seemingly simple design choices can have profound implications for safety, efficiency, and durability in our built environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Why can’t a round manhole cover fall into its own hole?
A round cover has a constant diameter across its entire shape. The opening it covers has the exact same diameter. Because there’s no way to orient a circle such that its dimension becomes smaller than its diameter, it physically cannot pass through its own opening. -
Are there any non-round manhole covers?
Yes, while rare for deep manholes, you might see square or rectangular access covers for utility boxes, electrical conduits, or telecommunication vaults, especially if they are shallow or hinged. However, for access to deep underground shafts where workers enter, round covers are overwhelmingly preferred due to safety. -
What are manhole covers made of?
Traditionally, they are made from cast iron due to its strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Modern covers can also be made from ductile iron, composite materials, or reinforced concrete, offering different benefits in terms of weight, corrosion resistance, or security. -
How heavy are manhole covers?
Their weight varies significantly based on size and material, but standard cast iron manhole covers can weigh anywhere from 50 kg (110 lbs) to over 150 kg (330 lbs). This weight helps them stay securely in place and resist vehicle traffic. -
Do manhole covers ever explode or pop off?
In rare instances, pressure buildup from explosive gases (like methane in sewers), steam, or electrical arcing in underground vaults can cause manhole covers to be dislodged or even "explode" upwards. While the round design is strong, extreme internal pressure can overcome its resistance. This is why proper ventilation and monitoring of underground systems are crucial.
Appreciating the Unseen Genius
So, the next time you step over one of those unassuming circles in the street, take a moment to appreciate the unsung hero of urban engineering. It’s not just a lid; it’s a meticulously engineered solution, a silent guardian ensuring safety, efficiency, and structural integrity beneath our bustling cities. It’s a testament to how even the most mundane objects can embody profound technological brilliance, proving that sometimes, the simplest shapes hold the deepest wisdom. It’s truly a perfect tech design, hiding in plain sight.





