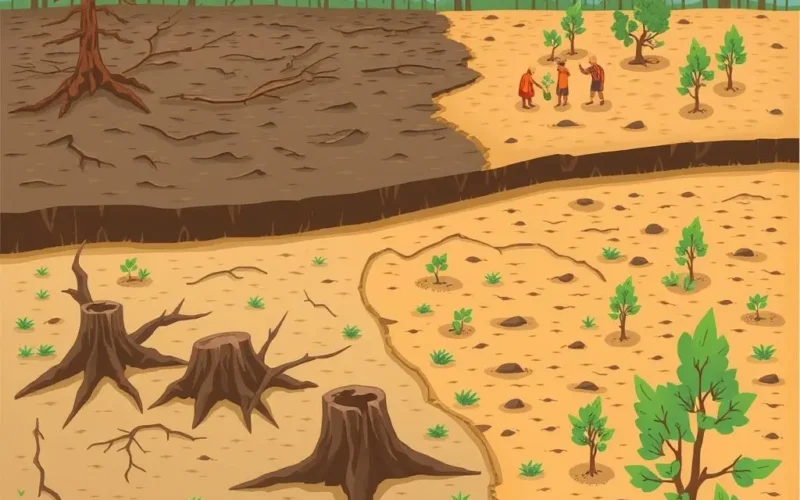
Ever stared at the vast, open wounds left by deforestation and felt overwhelmed by the sheer scale of the challenge? Planting billions, even trillions, of trees the traditional way feels like an uphill battle against the clock, especially when climate change is accelerating the need. But what if the solution wasn’t just on the ground, but soaring through the air?
Get ready to meet the future of forest restoration, because it’s arriving via drone. Imagine high-tech, robotic gardeners capable of navigating difficult terrains and deploying the building blocks of a new forest with impressive speed. These aren’t just concepts from a sci-fi movie; specialized seed-bombing drones are becoming a reality in the fight to re-green our planet.
Curious to see these aerial planters in action? We whipped up a quick look at what this innovative approach entails. Check out this short video:
Pretty neat, right? It’s literally innovation taking root from the sky. But there’s much more to unpack about how these flying robots are aiming to revolutionize reforestation efforts.
Table of Contents
The Colossal Challenge of Reforestation
Before we delve deeper into the tech, let’s consider the problem. Deforestation occurs at alarming rates globally, driven by agriculture, logging, wildfires, and urban expansion. Restoring these lost forests is crucial for biodiversity, climate regulation, water cycles, and supporting livelihoods. However, traditional manual tree planting is slow, labor-intensive, and often difficult or dangerous in remote, steep, or previously burned areas. Scaling up to the billions of trees needed globally feels daunting with conventional methods alone.

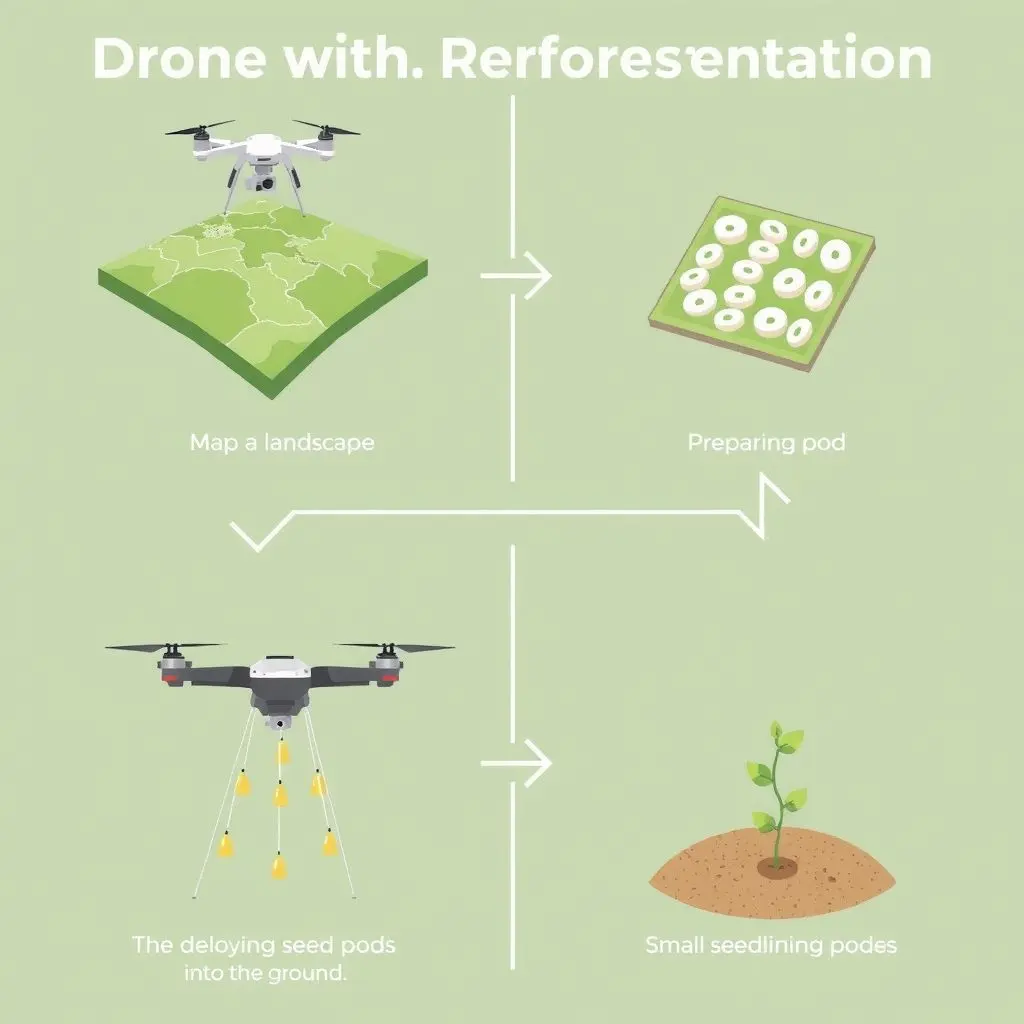
How Seed-Bombing Drones Work
This is where the ‘seed-bombing robots’ come in. Instead of human planters digging holes, drones are equipped with specialized mechanisms to dispense seed pods or pellets from the air. Here’s a breakdown of the typical process:
- Mapping and Planning: The area to be reforested is surveyed using mapping drones equipped with cameras and sensors. This data helps identify optimal planting spots, taking into account terrain, soil conditions, existing vegetation, and sunlight.
- Preparing the “Seed Bombs”: The seeds aren’t just dropped loose. They are typically encased in biodegradable pods or pellets often mixed with clay, nutrients, and sometimes hydrogel to retain moisture. These ‘seed bombs’ protect the seed from pests and harsh conditions and provide a initial boost for germination.
- Automated Deployment: Reforestation drones follow pre-programmed flight paths determined during the mapping phase. They use GPS and sometimes other sensors to navigate precisely and release the seed pods at calculated intervals and locations.
- Monitoring (Optional but Recommended): While the planting is automated, monitoring the success rate of germination and seedling growth often still requires some level of ground-based or supplementary drone-based inspection over time.
Different systems exist, from multi-rotor drones carrying dozens or hundreds of seed pods to fixed-wing drones or even helicopters adapted for aerial seeding over vast areas. The key is automating the dispersal process for speed and efficiency.
Advantages: Speed, Scale, and Safety
Why is this approach gaining traction? The benefits are compelling:
- Unprecedented Speed: Drones can cover significantly more ground in a day than human planters. Some systems claim planting rates many times faster than traditional methods.
- Access to Difficult Terrain: Steep slopes, rocky ground, marshlands, or areas recovering from fires (which can be hazardous due to unstable ground or lingering dangers) become accessible from the air.
- Precision Planting: Unlike broadcast seeding from aircraft, which can be inefficient, drones can often deploy seeds with greater precision to spots identified as having the best chance of success.
- Reduced Human Risk: Eliminates the need for human planters to navigate dangerous or remote environments.
- Potential for Scale: As technology matures, fleets of autonomous drones could theoretically cover massive areas, dramatically increasing the scale of reforestation possible.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential is huge, drone reforestation isn’t without its hurdles:
- Germination Success Rates: Dropping seeds from the air, even in protected pods, doesn’t guarantee germination and survival. Factors like soil type, moisture, competition from weeds, and wildlife predation play a significant role. Success rates can vary widely depending on the environment and seed bomb technology.
- Seed Bomb Technology: Developing seed pods that effectively protect the seed, provide nutrients, absorb moisture, and then biodegrade properly is complex and an area of ongoing research.
- Cost of Technology: While potentially cost-effective at scale, the initial investment in specialized drones, mapping technology, and seed bomb development can be significant.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Drones can plant, but young trees still need monitoring and sometimes maintenance (like weeding or protection) to ensure they survive and grow into a forest. This still often requires ground crews.
- Ecological Complexity: Reforestation isn’t just about planting trees; it’s about restoring complex ecosystems. Simply dropping seeds might not be suitable for all environments and might need to be part of a larger restoration strategy.
Disclaimer: The success rates of drone-based reforestation projects are still being evaluated and can vary significantly based on location, species, and the specific technology used. It’s a developing field, and real-world results are crucial for validating its long-term effectiveness.

The Path Ahead for Aerial Planters
Despite the challenges, the trajectory for drone-based reforestation is upward. Companies and organizations are actively developing more sophisticated systems, integrating AI for better site analysis and deployment, and refining seed bomb technology for higher success rates. Projects are underway in various parts of the world, targeting areas difficult to reach by traditional means.
The goal isn’t necessarily to replace human planters entirely, but to provide a powerful tool to accelerate efforts, reach inaccessible areas, and tackle the reforestation challenge at the massive scale required to make a meaningful impact on climate change and biodiversity loss.

Frequently Asked Questions About Reforestation Drones
Got more questions? Here are some common ones:
Q: How many seeds can a drone carry?
A: This varies greatly depending on the drone size and design, and the size of the seed pods. Smaller drones might carry a few dozen, while larger, more specialized systems could carry hundreds or even thousands of seed pellets per flight.
Q: How fast can they plant?
A: Speed claims vary, but some systems can deploy seeds much faster than manual labor, potentially covering hectares in a single day, depending on the drone’s payload capacity and the density of planting required.
Q: What kinds of seeds are used?
A: The seeds used are typically native species suitable for the specific ecosystem being restored. The seed pods are designed to protect these particular seeds and aid their germination.
Q: Is this cheaper than traditional planting?
A: The economics are still evolving. While the initial technology cost can be high, the speed and ability to access difficult areas might make it more cost-effective per successfully grown tree in certain scenarios, especially at scale. It’s often seen as a complementary method.
Q: What is the success rate of the seeds dropped by drones?
A: Success rates (germination and initial survival) are highly variable, influenced by climate, soil, seed viability, predation, and seed pod effectiveness. They are generally lower than planting saplings by hand but the sheer volume and speed of deployment aim to offset this.
Taking Flight Towards a Greener Planet
Using technology like seed-bombing drones offers a hopeful perspective on tackling immense environmental challenges. These robotic helpers, combined with ongoing research and traditional methods, are helping us reimagine what’s possible in the race to restore our planet’s vital forests. It’s a powerful example of how innovation, taking to the skies, can play a pivotal role in cultivating a healthier, greener future for everyone.




