We’ve all heard it, right? That age-old piece of tech wisdom that says if you want to squeeze every last drop of juice out of your phone’s battery, you absolutely *must* turn off Wi-Fi and Bluetooth the moment you’re not actively using them. For years, it was the go-to advice, passed down like some ancient digital commandment.
But let’s be real: Is this still true in the era of hyper-efficient chips and sophisticated power management? Or is it, dare we say, mostly a tech myth that’s long overstayed its welcome?
Table of Contents
The Myth Busted: Modern Chips Sip, They Don’t Gulp
Here’s the scoop: The idea that leaving Wi-Fi and Bluetooth on constantly drains your battery dry is largely outdated, especially for modern smartphones, tablets, and laptops manufactured in the last several years. The technology powering these features has advanced dramatically.
Think of the Wi-Fi and Bluetooth chips in your current device not like hungry power guzzlers, but more like tiny, well-behaved creatures that know how to conserve energy. When they aren’t actively transferring data (downloading files, streaming video, maintaining a Bluetooth connection), they enter incredibly low-power standby modes. They ‘sip’ power, checking periodically for known networks or paired devices without expending much energy at all.
This efficiency is due to advancements in semiconductor design, power management algorithms integrated into operating systems (like iOS and Android), and the move towards chipsets designed for mobile, battery-constrained environments. They are engineered to minimize power draw when idle.
Before we dive deeper into what actually drains your battery, check out this quick take on the myth:
What Really Devours Your Battery Life?
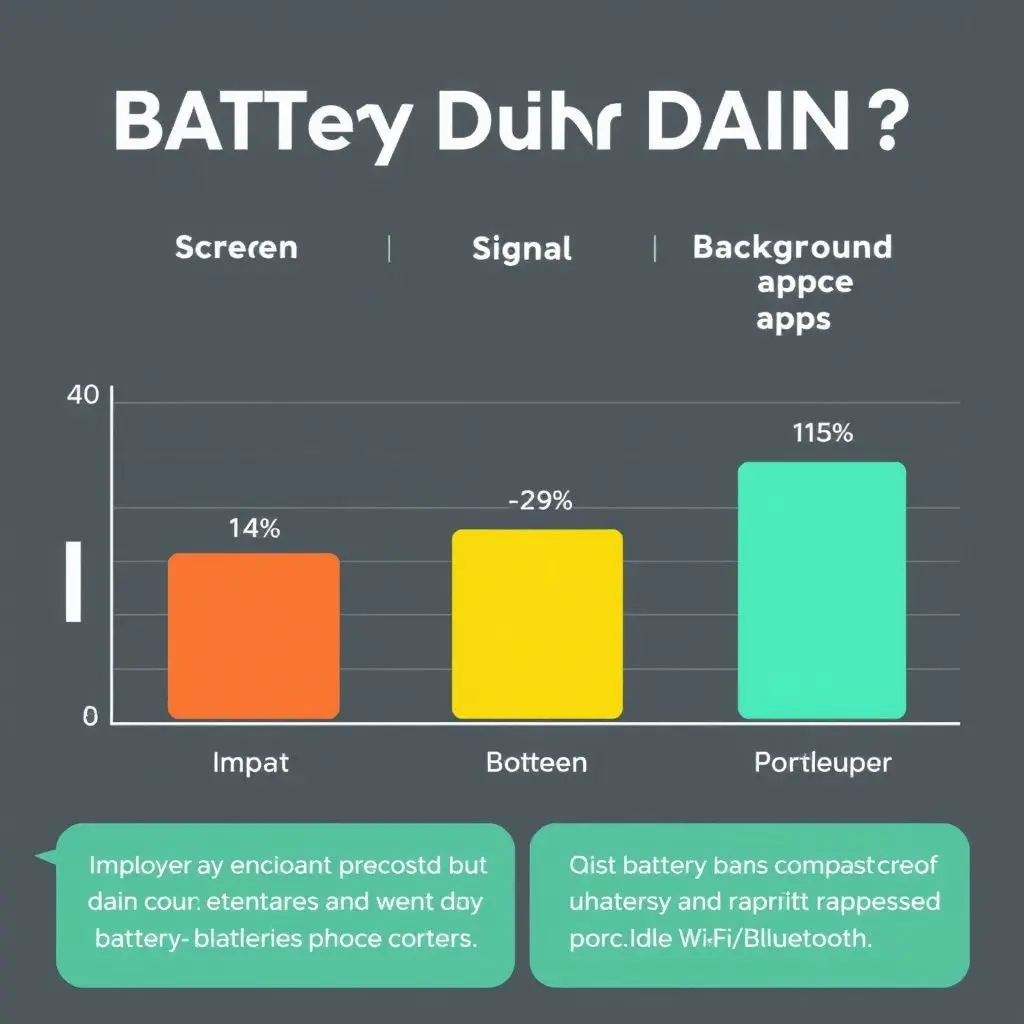
Now that we’ve established that idle Wi-Fi and Bluetooth aren’t the battery boogeymen they once were, let’s talk about the *real* culprits. These are the components and activities that actually make your battery percentage plummet throughout the day:
1. The Screen: The Brightest Battery Burner
This is hands down the number one battery drainer for most users. Your display, especially at high brightness levels, requires significant power to illuminate millions of pixels. The larger and brighter the screen, the more juice it consumes. Spending hours scrolling, watching videos, or gaming with the brightness cranked up will deplete your battery far faster than Wi-Fi or Bluetooth ever could.
2. Background App Activity: The Silent Killers
Many apps continue to work even when you’re not actively using them. They might refresh content, check for updates, track your location, or send you notifications. While operating systems have gotten better at managing background processes, poorly optimized or resource-hungry apps can still consume considerable power without you even realizing it. Check your phone’s battery usage settings – you might be surprised which apps are using the most power in the background.
3. Cellular Signal Strength: The Desperate Search
When your phone is in an area with poor cellular signal, it has to work much harder to connect to the network. It constantly boosts its transmitter power in a frantic search for a stable connection. This struggle consumes a significant amount of battery. If you’re in a basement, rural area, or anywhere with spotty coverage, your phone’s radio is likely working overtime, draining the battery far more than searching for a Wi-Fi network would.

4. Location Services (GPS): Pinpointing Your Position
GPS requires substantial power to communicate with satellites and determine your precise location. Apps that frequently request your location (mapping apps, social media, fitness trackers) can be significant battery drains, especially when used for extended periods or when set to ‘always allow’ location access.
5. Processor Usage: Heavy Lifting
Running demanding tasks like playing graphics-intensive games, editing videos, or multitasking heavily puts a strain on your device’s processor (CPU and GPU). Higher processor activity directly translates to higher power consumption.
Idle vs. Active Power Draw: Understanding the Difference
It’s crucial to understand the difference between idle power consumption and active power consumption. While modern Wi-Fi and Bluetooth chips use very little power when idle (just listening or in a low-power state), they do consume more power when actively transmitting or receiving data. However, even active data transfer is often less impactful than the constant power draw of a bright screen or a struggling cellular radio.
Turning off Wi-Fi might save a *tiny* bit of power by preventing the occasional background network check or accidental connection, but the saving is often negligible compared to the factors listed above.
Is There EVER a Time to Turn Them Off?
For the vast majority of users with modern devices, the power saved by manually toggling Wi-Fi and Bluetooth off when not in use is so minimal it’s not worth the effort or the loss of convenience. Leaving them on allows for seamless connectivity to known networks, quick pairing with devices like headphones or smartwatches, and features like Wi-Fi-based location accuracy.
Perhaps on a very old device (many years old) with outdated chips, or in an extreme scenario where you are trying to eke out every possible minute from a critically low battery and every single process matters, you *might* see a marginal benefit. But for everyday use on contemporary phones? It’s simply not a significant factor.
Focus on What Actually Works: Real Battery Saving Tips
Instead of stressing about those Wi-Fi and Bluetooth toggles, focus your energy on these strategies for genuine battery conservation:
- Reduce Screen Brightness: Use auto-brightness or manually lower it. Shorter screen timeout settings also help.
- Manage Background App Refresh: Limit which apps can refresh content in the background in your device settings.
- Identify and Manage Power-Hungry Apps: Check battery usage statistics in settings and restrict or uninstall apps that are consuming excessive power.
- Improve Cellular Signal: If possible, move to an area with better reception. On some devices, you can temporarily switch to 3G or 2G in areas with poor LTE coverage, though this isn’t always practical.
- Limit Location Services: Set location access for apps to ‘While Using’ or ‘Ask Next Time’ rather than ‘Always’ unless absolutely necessary.
- Use Battery Saver Mode: Most devices have a low power or battery saver mode that automatically adjusts settings to conserve energy when your battery is low.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Does connecting to Wi-Fi save battery compared to using cellular data?
A: Generally, yes. Using Wi-Fi for data transfer is often more power-efficient than using cellular data, especially for large downloads or streaming. Your phone’s cellular radio consumes significant power, particularly with weaker signals.
Q: Does keeping Bluetooth on while not connected drain battery?
A: Very little on modern devices. When not actively paired or transferring data, the Bluetooth chip is in a low-power scanning or advertising mode that uses minimal energy.
Q: Should I close all my apps to save battery?
A: Not necessarily. Modern operating systems are designed to manage apps in the background efficiently. Force-closing apps repeatedly can sometimes use *more* power as the device has to completely reload them each time you open them. Focus on managing background refresh and identifying truly problematic apps.
Q: Does searching for a Wi-Fi network use a lot of battery?
A: When actively scanning for *new* networks (like when Wi-Fi is off and you turn it on in a new location), it uses more power than just being connected or being in standby. However, the power used when Wi-Fi is left on and occasionally checks for known networks is very low.
Moving Beyond the Old Advice
So there you have it. The myth about turning off Wi-Fi and Bluetooth to save significant battery life on modern devices is largely just that – a myth. While every milliwatt counts in theory, the power savings from this specific action are typically dwarfed by the consumption of your screen, background apps, and cellular signal strength.
Stop the unnecessary toggle-gymnastics and enjoy the convenience of seamless connectivity. Focus your battery-saving efforts on the factors that truly make a difference, and let your modern device’s efficient chips do their thing in the background.